The COVID-19 health crisis had a greater impact on demand for commercial real estate than the Great Recession, as mandatory quarantines, social distancing, shutdowns, supply chain disruptions, unemployment and an erosion of consumer confidence brought the industry to its knees in 2020 and through the first quarter 2021.
One bright spot in the troubled commercial real estate sector has been healthcare real estate. While office visits for elective procedures plummeted, critical care, particularly off-campus, saw a surge as a result of the pandemic, balancing any weaknesses in the sector.
The U.S. Medical Office (MOB) vacancy rate was 8.6% as of Q4 2020, up from 7.8% at the end of 2019. In comparison, the overall office sector vacancy rate was 13.2% as of Q4 2020, sales volumes have held up extremely well, and real estate investors remain very bullish on the sector.
“The healthcare sector continues to play a dominant role in the US economy and has displayed year-on-year growth for many decades,” notes Martin Freeman, CEO of OrbVest, a global real estate company that invests in US income producing medical commercial real estate. “From an economic and political perspective, the new Biden administration is strongly in favor of expanding healthcare services and benefits and we remain bullish on the sector going forward.”
Expectations for continued outperformance in the healthcare real estate sector is buoyed by some of the following fundamentals.
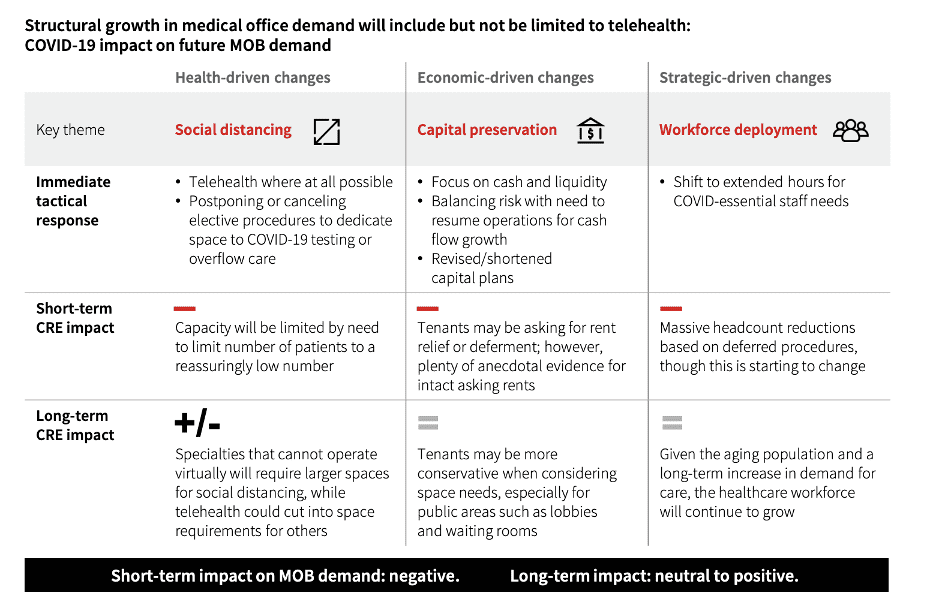
1. Structural Growth In Medical Office Demand Will Include, But Not Be Limited To Telehealth
Investors in healthcare real estate have to consider the impact of health-driven changes, economic-driven changes, and strategic-driven changes. Telehealth will be a great driver of healthcare real estate growth and be complementary rather than competitive. Take telehealth giant Teladoc’s merger with chronic disease manager Livongo, for example.
Social distancing, whether popular or not, will be a growth driver for structural and spatial improvements in medical office buildings, as consumers and staff will require modifications to feel safe. Economically, capital preservation will impact real estate, and strategically, workforce deployment could be impacted. There could be some short-term disruption as we figure out how to take what worked with the “old normal” and integrate with the “new normal.” We should not be surprised to see limited capacities, rent relief or deferment, headcount reductions based on deferred procedures, and more.
However, long-term, as the sector will inevitably adapt and adjust, and healthcare real estate should have solid long-term growth potential because of shifting consumer needs and evolving demographics.
 (Source: JLL)
(Source: JLL)
2. Increased Real Estate Demand From The Segmentation Of Wellness And Acute Care Locations
“We are seeing a measurable shift from the hospital as the center of American healthcare,” explains Freeman, “this trend is likely to continue and accelerate in future years.”
This is another tailwind for healthcare real estate partially driven by demographics. The need for preventive and personalized care among millennials and seniors was already reshaping healthcare real estate long before the pandemic. We already discussed how America’s aging demographics appear to directly correlate with increased real estate demand for health services. Providers also understand that both millennials and seniors value preventive and personalized care. They know that these cohorts want to focus on leading a long and healthy life for themselves and their families. Plus, seniors now have access to less expensive and convenient care, while young working millennial parents have access to quicker and specialized care for their children. This has been working too well for it not to increase.
However, this trend is not exclusive to demographic shifts. Many of these triggers are due to rising hospital volume and how complicated they can be to navigate. Convenient access coupled with lifestyle integration look like a key driver. Hospitals will likely focus on higher acuity in-patient care over the long-term, opening up a need for additional real estate dedicated to lower-acuity, lower-cost facilities in more convenient and easily accessible locations in population centers.
Plus, with a brighter spotlight being shone on preexisting conditions, wellness and preventive care needs have never been higher. From a real estate standpoint, future outperformance will likely involve a combination of the following.
• Increased efficiency of outpatient facilities.
This can be considered a “medical home” model. This can include grouping primary care and specialty care in consolidated locations accompanying services such as imaging, pharmacy, and laboratories. This would also potentially require larger buildings with more giant footprints. The most significant providers have increasingly adopted this model already.
• The rise of “MedTail”
Retail and health real estate both share many commonalities, such as the need for high traffic, visibility, neighborhood proximity, and parking access. Shopping center availability and affordability are on the rise, and healthcare tenants may jump at the opportunity to increasingly relocate within retail centers.
This has given rise to a new segment of commercial real estate- “MedTail.” Retail locations with integrated healthcare options, such as drugstores are becoming increasingly prevalent.
According to healthcare real estate firm HBRE, small towns and suburban areas that once had little access to local medical facilities are seeing more options such as the CVS minute clinic or Kroger’s Little Clinic. Plus, urgent care centers have been popping up in retail strip malls as another offering to suburban residents.
Tether Advisors also performed a study and found that “nearly 80 percent of private equity, commercial real estate and retail healthcare respondents believe medtail investment will increase in the coming year and that COVID-19 bolstered the sector’s outlook.”
• Maximize revenue opportunities on a single site
Operators can maximize multiple revenue streams, such as promoting flexibility for different care delivery types at other times. Providers are also more willing to outsource facilities and project management services in strategic partnerships to ensure that they obtain the highest possible value from their real estate.
This could also create a significant real estate opening due to adjustments hospitals will have to make. COVID-19 increased the need for higher-acuity space within hospitals and pushed lower-acuity and administrative uses into alternative locations. This altered the functional mix of hospitals and heightened a public perception that hospitals are for very sick people. Many short- and long-term approaches affecting medical real estate should be seen here.
Hospitals will inevitably have to optimize their existing real estate and reduce the potential for contamination by modifying existing spaces and consolidating. They will also have to embrace higher-acuity care while managing contagion risk- even once the pandemic becomes more manageable. Future success for hospitals will also involve embracing the shift to higher-acuity care and easing safety concerns within hospital facilities.
3. Medical Office Investments Are A Source Of Stability Pre-Pandemic, Mid-Pandemic, And Post-Pandemic
The numbers don’t lie. Medical office buildings (MOBs) are loved by passive investors because of long-term leases, stable occupancy, consistent income streams, and tenant quality. This asset class has many tailwinds blowing in its favor for both the short-term and long-term.
First and foremost, these properties greatly benefited from all of the aid in the multiple stimulus packages and the trillions dedicated to helping small businesses. Think of all the independent physicians and small practices that have benefited from the PPP loans. While many tenants struggled to pay rent, most of these medical tenants were absolutely fine. Loans from the federal government required hospitals to maintain staffing levels and continue to pay rent on their buildings, and as a result relatively few organizations had trouble making rent. In fact, in the worst part of the pandemic, medical office space owners collected rent from tenants in the high 90 percent range. As a result of the relatively low amount of rent deferrals, there’s a strong long-term outlook for healthcare real estate.
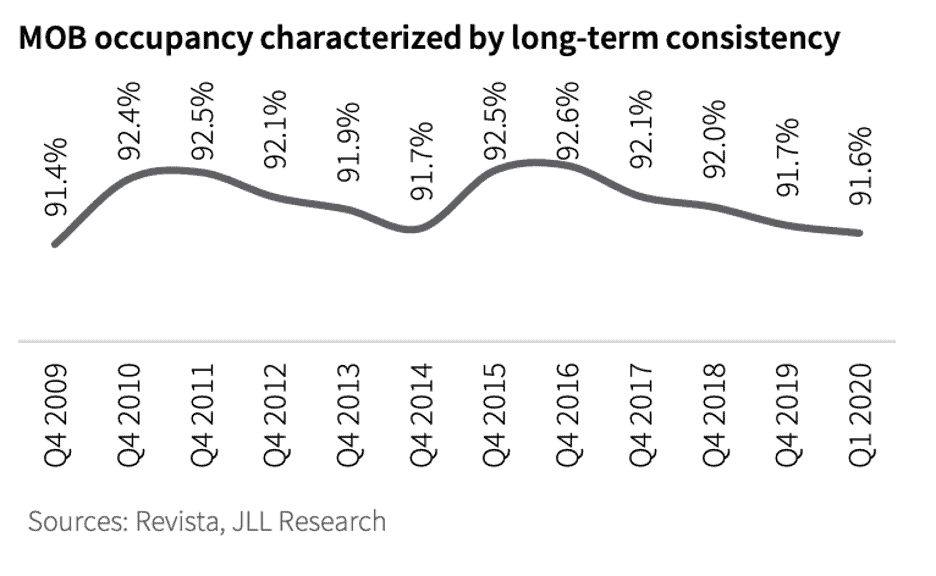
Consider MOB fundamentals and occupancy rates too. Across approximately 1.5 billion square feet in the United States, MOB occupancy has been remarkably stable. Between the financial crisis and now, MOB occupancy has fluctuated between 91.4 percent and 92.6 percent. Compare that to the average occupancy rate for offices in the U.S. in that same period- roughly 82.1 percent to 85.8 percent.
 Or maybe you want to consider tenant retention. Because of the high investment in infrastructure required by medical tenants and barriers to entry such as regulations needed for surgery centers and imaging, MOBs on average report an average retention rate in the high 80 percent range, significantly surpassing typical commercial office retention.
Or maybe you want to consider tenant retention. Because of the high investment in infrastructure required by medical tenants and barriers to entry such as regulations needed for surgery centers and imaging, MOBs on average report an average retention rate in the high 80 percent range, significantly surpassing typical commercial office retention.
Plus, despite all of the economic headwinds and the downturn in commercial real estate, new outpatient medical space construction has remained consistently stable at around 17 to 20 million square feet a year, roughly 1.8 percent of inventory nationally, and well below the national average of 2.1 percent for commercial office.
There is also virtually no speculative medical office development either, with most developers and lenders alike demanding pre-leasing of 50 percent to launch new construction.
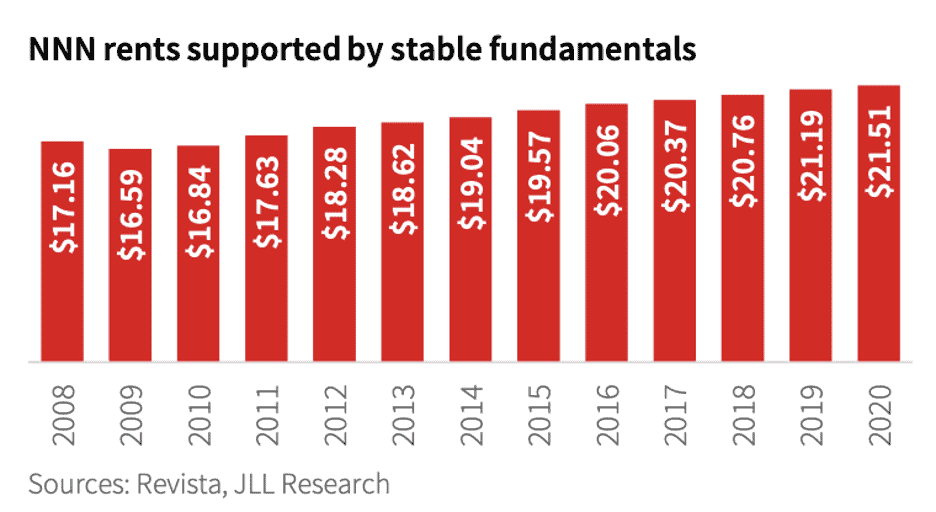
Look at how medical rent growths have grown too. Nationally, the average medical office net rents steadily rose from $18.28 per square foot in 2012 to $21.51 in early 2020. This is a stable 1.5 percent year-over-year gain and 31.8 percent peak-to-trough return from the low of $16.32 in the fourth quarter of 2008.
Key Takeaway for Investors
Can healthcare real estate weather the commercial market’s downturn? The answer is a resounding yes.
“The current challenges faced by the global economy, and the potentially aggressive rebound in business sentiment in the US, creates an ideal opportunity for companies like OrbVest to assist investors from around the world to invest directly into medical real estate in the US and grow their wealth consistently and sustainably,” says Freeman.
Healthcare is changing, our demographics are aging, and if this past year showed us anything, it’s that an adaptable and forward-thinking health system is vital to a functional society. We will see numerous shifts in healthcare real estate and MOBs in the short-term and long-term. But the bottom line is that if you look at the fundamentals, you really cannot find a better long-term investment than healthcare real estate for stable income streams, quality tenants, long-term leases, and high occupancy rates.
If you look at investor activity since the financial crisis, this supports the sector’s fundamentals. This is a durable asset class, changing with the times, and a property type that will experience growth far into the future. If you are looking for passive income in real estate, healthcare commercial real estate offers an extraordinary investment opportunity.
Source: NuWire Investors
 Forecasted growth in patient care volumes between 2020 and 2030, however, show divergent trends between inpatient and outpatient utilization. Inpatient admissions are expected to decline in absolute number from 34.9 million stays to 34.6 stays, or a drop of 0.9% in this 10-year period.
Forecasted growth in patient care volumes between 2020 and 2030, however, show divergent trends between inpatient and outpatient utilization. Inpatient admissions are expected to decline in absolute number from 34.9 million stays to 34.6 stays, or a drop of 0.9% in this 10-year period.






